Principle for Ametropic Correction of iLASIK Surgery
Procedures of Surgery
Introduction to Characteristic of Various Equipments
Selection of Surgery (Indication and Price)
Dos and Don'ts before and after Surgery

Procedures of Surgery
Step 1 (measure the diopter) is divided into following two kinds:

Utilize computer Autorefractor to determine the diopters within ±0.25D deviation and base on precise optometry to calculate the optimal correction diopters before surgery. 2. Individualized Measurements
Use WaveScan to measure and make out a precise eyeball aberration diagram for the purpose of individual exclusive vision correction calculation before surgery. (Including high-level and low-level aberration)
Step 2 (make a corneal flap) is divided into following two kinds:
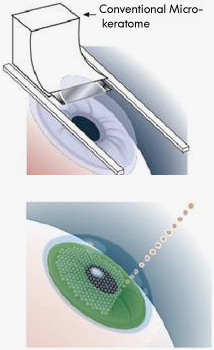
1. Corneal Flap Making by Micro-keratome
Doctors use hand-held equipment with a vibrating metal blade (called as fully automatic Micro-keratome) to cut a corneal flap with 8.5mm of diameters on 1/4 – 1/3 upper part of cornea which is about 110–160um of thickness, and then lift this corneal flap, during which the corneal epithelium and Bowman’s membrane must be remained. 2. Corneal Flap Making by Laser
2. Corneal Flap Making by Laser
INTRALASE only takes 10s to make a corneal flap in cornea by use of laser beam of near infrared light (1,053mm), which totally eliminate the harm to cornea caused by conventional blade.
The laser beams are accurately focused on corneal endothelium, each beam will form a bubble. These bubbles would form a line from points, and then become a flat surface constituted of thousands of small bubbles, thereupon, a smooth corneal flap is formed.
Doctors use hand-held equipment with a vibrating metal blade (called as fully automatic Micro-keratome) to cut a corneal flap with 8.5mm of diameters on 1/4 – 1/3 upper part of cornea which is about 110–160um of thickness, and then lift this corneal flap, during which the corneal epithelium and Bowman’s membrane must be remained.

INTRALASE only takes 10s to make a corneal flap in cornea by use of laser beam of near infrared light (1,053mm), which totally eliminate the harm to cornea caused by conventional blade.
The laser beams are accurately focused on corneal endothelium, each beam will form a bubble. These bubbles would form a line from points, and then become a flat surface constituted of thousands of small bubbles, thereupon, a smooth corneal flap is formed.
Step 3 (refractive correction by laser) is divided into following two kinds:
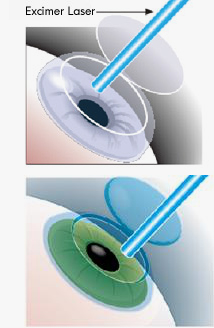
1. Correction by Conventional Laser (Excimer Laser)
Lift the corneal flap and use Excimer Laser to correct the vision; and then move the corneal flap back to original position after laser, thereupon, the whole surgery is finished. 2. Correction by Wave Front
2. Correction by Wave Front
Lift the corneal flap and use IR Fourier wavefront laser to change the diopters for optimal vision, and then move the corneal flap back to original position after laser, thereupon, the whole surgery is finished.
Lift the corneal flap and use Excimer Laser to correct the vision; and then move the corneal flap back to original position after laser, thereupon, the whole surgery is finished.

Lift the corneal flap and use IR Fourier wavefront laser to change the diopters for optimal vision, and then move the corneal flap back to original position after laser, thereupon, the whole surgery is finished.